About Us
At TwentyOne Sugars , We are dedicated to producing high-quality sugar that exceeds industry standards. With a history of our sugar production, our experienced team has developed a reputation for excellence in the sugar manufacturing industry.

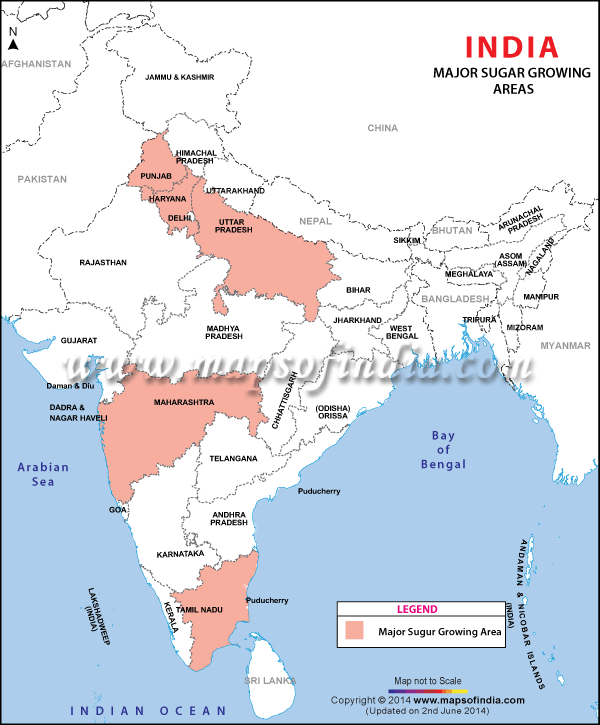
Our Sugar Industry Units
in India
Our state-of-the-art facility is equipped with the latest technology and machinery, ensuring that our sugar is produced with precision and consistency. We source only the finest sugar cane from trusted local farmers, and our strict quality control measures ensure that every batch meets our high standards.
In addition to producing sugar, we are also committed to sustainability and environmental responsibility. We use renewable energy sources, implement efficient waste management practices, and make efforts to reduce our carbon footprint.
Our goal is to provide our customers with the best possible product, and our dedicated team is always working to improve and evolve our processes. With a commitment to quality, sustainability, and customer satisfaction, TwentyOne Sugars is the ideal choice for all your sugar needs.
Types Of Sugar
Crystal Sugar :
This type of sugar is produced by crystallizing the syrup obtained from sugar cane or sugar beet juice. It is commonly used in baking and cooking.
Powdered Sugar :
Also known as confectioner's sugar, this type of sugar is made by grinding crystal sugar into a fine powder. It is often used for making icing and dusting baked goods.
Liquid Sugar :
This type of sugar is a solution of sugar in water, typically used for sweetening beverages and making syrups.
History of Sugar
The History of Sugar has Five main Phases:
1. The extraction of sugar cane juice from the sugarcane plant, and the subsequent domestication of the plant in tropical India and Southeast Asia sometime around 4,000 BC.
2. The invention of manufacture of cane sugar granules from sugarcane juice in India a little over two thousand years ago, followed by improvements in refining the crystal granules in India in the early centuries AD.
3. The spread of cultivation and manufacture of cane sugar to the medieval Islamic world together with some improvements in production methods.
4. The spread of cultivation and manufacture of cane sugar to the West Indies and tropical parts of the Americas beginning in the 16th century, followed by more intensive improvements in production in the 17th through 19th centuries in that part of the world.
5. The development of beet sugar, high-fructose corn syrup and other sweeteners in the 19th and 20th centuries.
Sugar was first produced from sugarcane plants in India sometime after the first century AD. The derivation of the word "sugar" is thought to be from Sanskrit शर्करा (śarkarā), meaning "ground or candied sugar," originally "grit, gravel". Sanskrit literature from ancient India, written between 1500 and 500 BC provides the first documentation of the cultivation of sugar cane and of the manufacture of sugar in the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent.


Geography of Sugar
Sugar is produced in over 120 countries from either sugar cane or sugar beet. Globally, approximately 80% of sugar is produced from sugar cane, and the remaining from sugar beet.
The sugar industry which encompasses 599 operating sugar mills, 309 distilleries and 180 cogeneration plant and numerous pulp, paper and chemical making units is supported by four leading sugarcane research institutions, twenty-two state sugarcane research stations, world class sugar machinery manufacturers, suppliers and technical experts. Currently, the industry produces around 300–350 million tonnes (Mt) cane, 20–22 Mt white sugar and 6–8 Mt jaggery and khandsari to meet the domestic consumption of sweeteners. Besides, about 2.7 billion liters of alcohol and 2,300 MW power and many chemicals are also produced.
Growing Sugar Cane :
Sugar cane is a tropical plant, and can only be grown in countries where there are average temperatures of 24°C (75°F) (e.g. near the equator), combined with strong sunshine and either heavy seasonal rainfall or plentiful supplies of water for irrigation. Major cane sugar regions include Brazil, India, China, Thailand, Australia, South Africa, Mexico and Guatemala.
When sugar cane is harvested, it has a sugar content of approximately 14% by weight, depending on the variety of sugar cane and geographical location. Its sugar content also varies from season to season.
Departments
Raw Materials
Sugar cane is a tall tropical grass that is grown mainly in countries with warm climates such as Brazil, India, and Thailand. Sugar beets are a type of root vegetable that is grown mainly in temperate climates such as Europe, North America, and Russia.

Both sugar cane and sugar beets are processed to extract their juice, which is then purified and concentrated to produce sugar. In some factories, molasses, a byproduct of the sugar production process, is also stored as a raw material for further processing into other products such as ethanol.
How sugar is made...
Sugar is typically made from sugar cane or sugar beet plants. The general process is as follows:
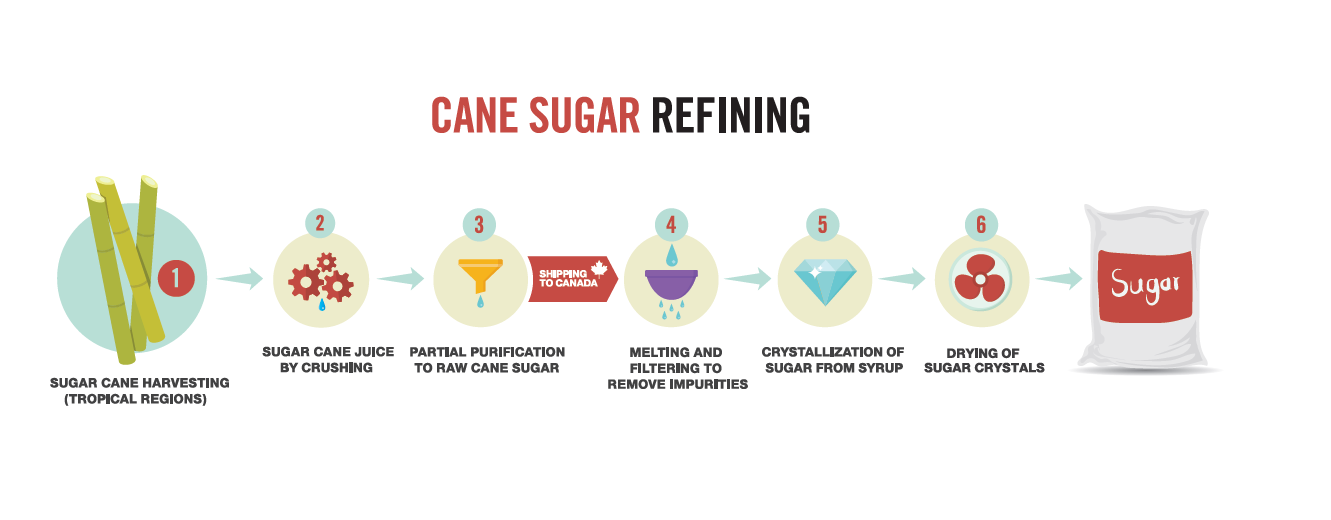
Firstly, The juice is extracted from the sugar cane or sugar beet through a process of crushing and pressing. The juice is then clarified to remove impurities such as dirt, leaves, and fibers. The clarified juice is then concentrated through boiling to remove water, producing a thick syrup.
The syrup is then cooled and seeded with sugar crystals, causing the sugar to form solid particles. The sugar crystals are then separated from the syrup through a centrifugation process. The sugar crystals are then washed, dried, and screened to remove any remaining impurities. And then lastly, The purified sugar crystals are then packaged and transported for distribution and sale.
Packaging :

The purified sugar crystals are packaged into our branded large and small paper bags and glass jars. We also consider the environmental impact of the packaging, such as using biodegradable materials or by reducing the packaging waste. Ultimately, our goal is to provide a convenient and attractive packaging solution for our sugar product. Then this packaged Sugar is transported for distribution and sale.
Our Business
Sugar Operations - Farm to Farm
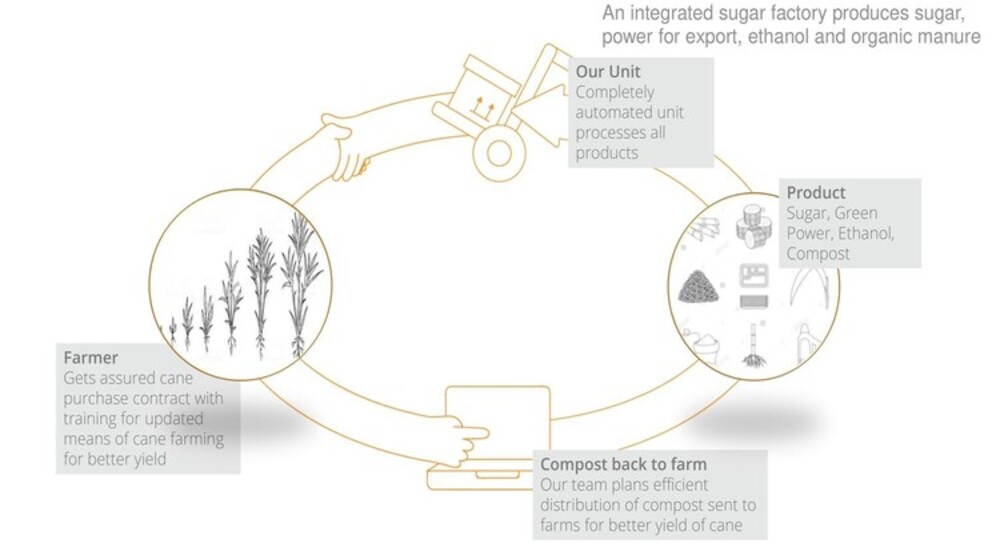
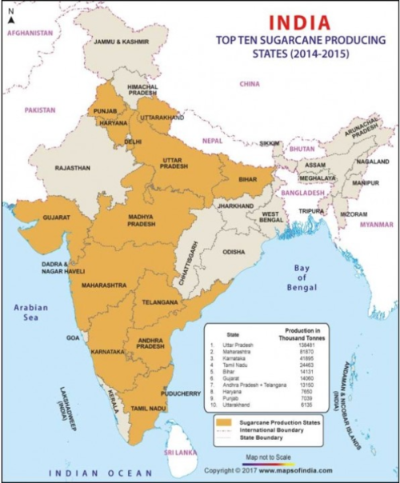
INDIA - The largest consumer of our product
Sugar industry is the second largest agro-based industry in India and contributes significantly to the socio-economic development of rural population. It supports 50 million farmers and their families and provides direct employment to over 0.5 million skilled and semi-skilled persons in sugar mills and integrated industries.
- Industry size : ₹ 105,000 Cr (US$ 15 Bn)
- Farmers : 50 Million (5 Million Workers)
- Planted area : 5 Million Hectares with 415 MMT of sugarcane
- Operating Mills : 525 ( Private - 50%, Co-op – 44%, Others 6%)
- Production : 80% UP, Maharashtra, Karnataka
- Consumption : 26 MMT per capita 19 kg.
Our Future Plans

Future Product Expansion
Refined Sugar
2G Ethanol
Lignin
Glycol Ethers
Constant R&D
We intend to develop an inhouse team of experts for constant
innovation in the sector on the raw material,
production and the raw material side.

The Green Revolution
- World Population will grow by 40% in 2050 and which is another 2.5 billion people. They need to eat and also power their lives. This means the power requirement will likely be double by then. Unless green power generation is encouraged, Co2 emissions contributing to global warming could increase by 80%. Thus, need for low carbon solutions for food / energy are equivalently important. A sugar plant uses Soil + Sunshine + Water to generate power and that too as a by product.
- Sugar Cane, as it grows, stores energy in two ways :
- Sucrose - a high-energy sweetener.
- Cellulose - the plant matter in leaves and straw.
- Some of that stored energy becomes sugar and the innovation unlocks for more renewable products that include
- ethanol from sugar cane juice – an affordable transportation fuel that cuts CGH emissions by 90% on average. With this the state of Maharashtra can replace 50% of fuel guzzling vehicles to ethanol consuming green vehicles.
- Cane Ethanol as an alternative for a cleaner planet – Thanks to Biotechnology that now permits conversion of cane juice to Ethanol. Ethanol’s full potential shall be unleashed with cellulosic biofuel which will be even cleaner and double the volume of fuel produced with the same amount of land.
- The next frontier is renewable hydrocarbons and bioplastic where sugarcane is converted to sustainable biochemicals and fuels. This will help creating a unique and green replacement for diesel / plastic.
- The above shall help to lower Co2 emissions, generate employment, reduce use of petroleum and above all create a healthier, cleaner planet.
Gallery
Frequently Asked Questioins
A Comprehensive Guide to Sugar: Answering Your Most Pressing Questions.
-
What is the process of sugar production?
Sugar is produced from sugarcane or sugar beet through a series of steps including harvesting, milling, juice extraction, purification, evaporation, crystallization, and refining.
-
What are the main ingredients in sugar production?
The main ingredients in sugar production are sugarcane or sugar beet, water, and steam.
-
How is sugar packaged and stored?
Sugar is packaged in bags, boxes, or containers and stored in cool and dry conditions to prevent moisture and spoilage.
-
What are the health benefits of sugar?
Sugar provides a quick source of energy, aids in digestion, and contributes to the overall taste and enjoyment of food.
-
What are the different types of sugar available?
There are several types of sugar available, including white sugar, brown sugar, raw sugar, powdered sugar, and liquid sugar.
-
What is the shelf life of sugar?
The shelf life of sugar is indefinite if stored properly in a cool and dry place. However, it may start to clump and become difficult to use if exposed to moisture.